CAMELS Rating System
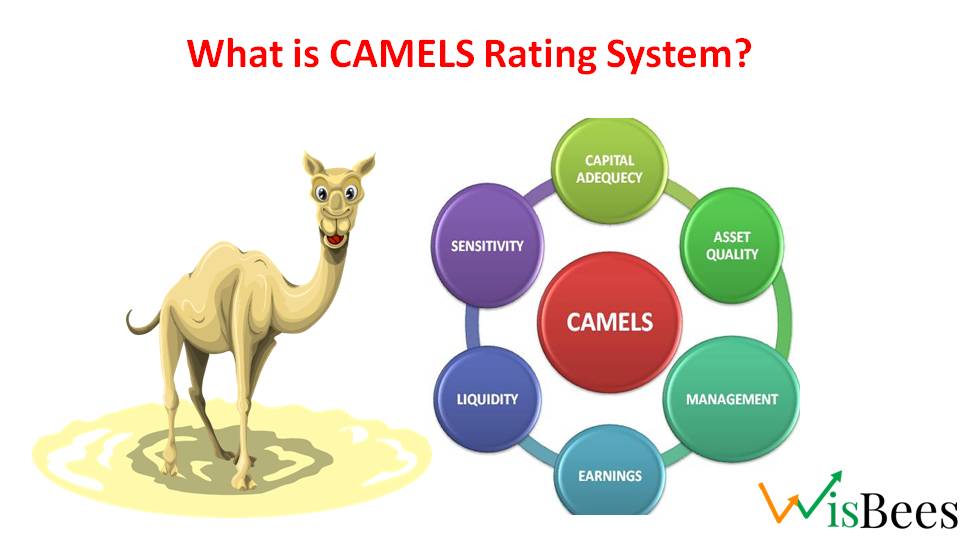
CAMELS rating system is a way to check how good a bank is in India. It is a supervisory rating system used by banking authorities to assess the financial condition of banks and other financial institutions. The CAMELS acronym stands for:
- Capital adequacy
- Asset quality
- Management
- Earnings
- Liquidity
- Sensitivity to market risk
In the following paragraphs, we have elaborated on each of these factors.
Who Uses CAMELS Rating System in India?
the CAMELS rating system is used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which is the central bank and the regulator of banks in India. The RBI uses the CAMELS rating system to review the risk levels of banks and to supervise them.
The bank managers also use the CAMELS rating system to understand their strengths and weaknesses and to take corrective actions. The CAMELS rating system is not used by the public or by other entities.
What is the Rating system?
Each component of the CAMELS rating system is assigned a score of 1 to 5, with 1 being the best score and 5 being the worst score. The overall CAMELS rating is then calculated by averaging the scores for the six components.
A CAMELS rating of 1 indicates that a bank is in excellent financial condition, while a rating of 5 indicates that a bank is in very poor financial condition. Banks with CAMELS ratings of 4 or 5 are considered to be "problem banks" and may be subject to regulatory intervention.
The CAMELS rating system is a valuable tool for regulators to assess the financial condition of banks and other financial institutions. The system helps regulators identify banks that are at risk of financial problems and take steps to prevent those problems from becoming worse.
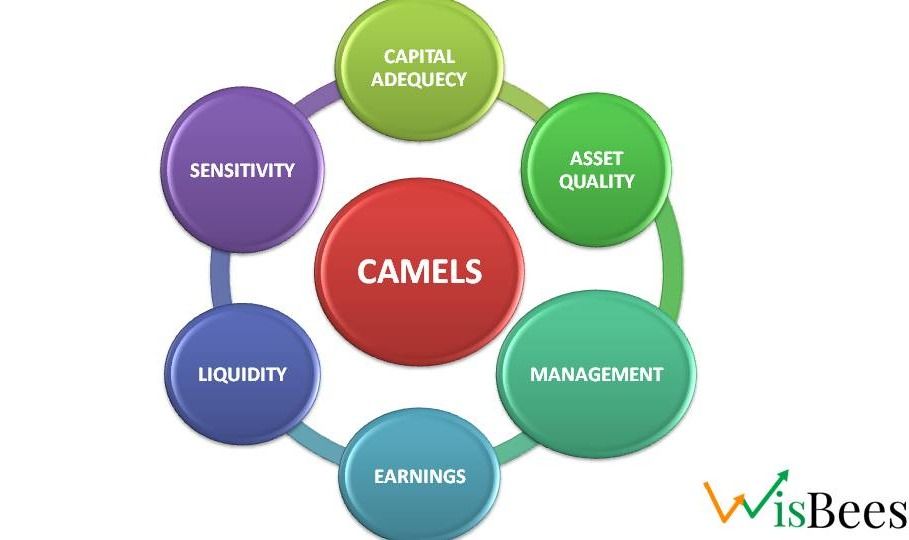
Explaining C-A-M-E-L-S
The CAMELS factors are:
- Capital adequacy: How much money the bank has to cover its losses and meet the minimum requirements set by the regulators.A bank with a high level of capital is considered to be more financially stable than a bank with a low level of capital.
- Asset quality: How safe and valuable the bank’s loans, investments, and other assets are, and how well the bank manages the risk of not getting paid back or losing money on them.
- Management: How well the bank is run by its leaders, managers, and staff, and how they plan, perform, control, and follow the rules. A bank with a strong management team is considered to be more financially stable than a bank with a weak management team.
- Earnings: How much profit the bank makes from its activities, how stable and growing its income is, how well it controls its costs, and how much money it sets aside for future needs and risks. Profitable banks are more likely to be able to withstand financial problems.
- Liquidity: How easily the bank can get money when it needs, without depending too much on outside sources, and how well it manages its cash flow and reserves. Liquidity is important because it allows banks to meet the demands of their depositors and other creditors
- Sensitivity: How much the bank is affected by changes in the market, such as interest rates, exchange rates, commodity prices, and stock prices, and how well it measures, monitors, and handles these changes.
| Broker | Type | Offerings | Invest |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Discount Broker | Mutual Funds, Stocks, IPOs, Bonds | Know more |
 |
Discount Broker | Mutual Funds, Stocks, IPOs, Bonds | Know more |
 |
Discount Broker | Mutual Funds, Stocks, IPOs, Bonds | Know more |
 |
Service Broker | Mutual Funds, Stocks, IPOs, Bonds | Know more |